What Is CRM Software? Complete Guide for Business Leaders 2024
Understand CRM software selection, implementation risks, pricing models, and decision frameworks. Expert guidance for SMBs, scale-ups, and enterprises choosing the right CRM system.
# What Is CRM Software and How Does It Work? A Strategic Guide for Business Decision-Makers
**SEO Title**: What Is CRM Software? Complete Guide for Business Leaders 2024
**Meta Description**: Understand CRM software selection, implementation risks, pricing models, and decision frameworks. Expert guidance for SMBs, scale-ups, and enterprises choosing the right CRM system.
**Keywords**: CRM software, CRM selection guide, CRM implementation, CRM pricing models, customer relationship management, CRM decision framework
---
## Expert Quick Answer
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software is a centralized platform that helps organizations manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and relationship data across teams. Beyond basic contact management, modern CRM systems serve as strategic infrastructure for revenue operations, integrating sales automation, marketing workflows, customer service, and analytics. The right CRM choice depends on your organization's scale, technical capabilities, compliance requirements, and long-term growth trajectory—not just feature checklists.
---
## Why CRM Software Is a Critical Business Decision, Not Just a Tool Purchase
In my 15 years of advising businesses on software selection, I've observed that organizations often approach CRM evaluation as a "feature comparison exercise" rather than a strategic infrastructure decision. This mindset leads to costly mistakes: budget overruns, low adoption rates, and expensive migrations within 18-24 months.
**CRM software is fundamentally different from other business tools** because it becomes the system of record for your most valuable asset—customer relationships. Once implemented, your CRM touches every customer-facing team, stores years of interaction history, and shapes how your organization scales revenue operations. A poor CRM choice doesn't just waste budget; it creates organizational debt that compounds over time.
Consider these realities from actual CRM implementations:
**Budget Impact**: While initial CRM subscriptions may start at $10-30 per user/month, the total cost of ownership (TCO) typically runs 3-5x higher when factoring in data migration, integrations, training, customization, and scaling costs. Organizations frequently discover hidden costs only after commitment—additional user tiers, API rate limits, premium support fees, and compliance add-ons.
**Adoption Risk**: Research consistently shows that 30-40% of CRM implementations fail due to low user adoption. When sales teams resist using a CRM, the system becomes a "data graveyard" rather than a strategic asset. This isn't just about training—it reflects fundamental misalignment between the CRM's design philosophy and your team's actual workflow.
**Vendor Lock-in**: CRM platforms create significant switching costs through proprietary data structures, custom workflows, and integration dependencies. Organizations that choose poorly often find themselves trapped in a system that no longer fits their needs, facing migration costs that exceed $50,000-$200,000 for mid-sized companies.
**Compliance and Security**: For organizations operating in regulated industries or serving global markets, CRM selection intersects with data residency requirements, GDPR compliance, SOC 2 certifications, and industry-specific regulations (HIPAA, FINRA, etc.). These constraints significantly narrow viable options and require upfront due diligence.
The stakes are high because **CRM software is not easily reversible**. Unlike project management tools or communication platforms, you cannot simply "switch CRMs" without significant business disruption. This reality demands a more rigorous, risk-aware evaluation process.
---
## How Businesses Should Evaluate CRM Software: A Decision Framework
Most CRM selection guides present feature checklists without explaining *how to think about trade-offs*. In practice, no CRM excels at everything—you're always choosing between competing priorities. Here's the systematic framework I use when advising clients:
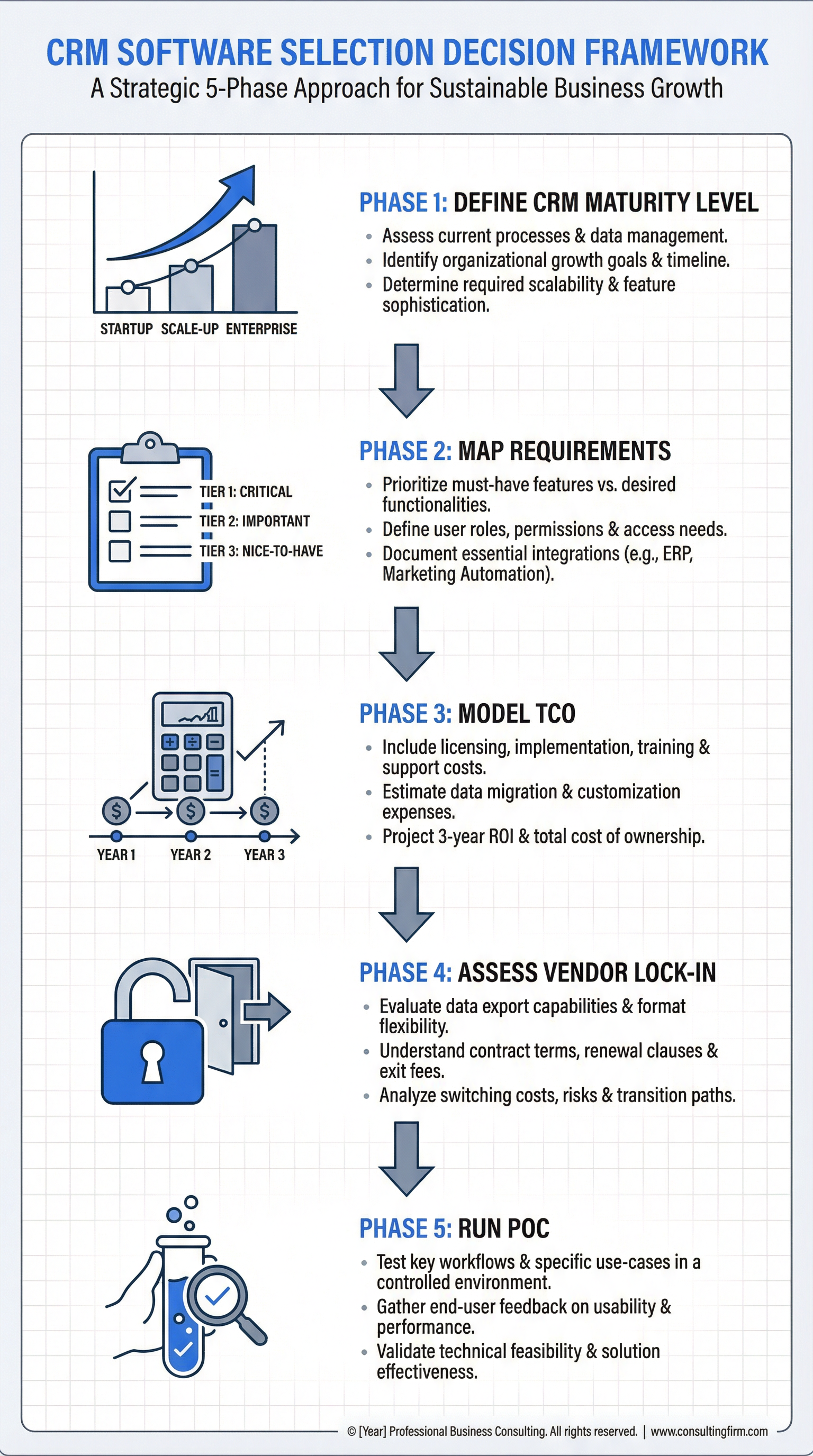
**Phase 1: Define Your CRM Maturity Level and Growth Trajectory**
Before evaluating any specific CRM, assess where your organization sits on the CRM maturity spectrum:
**Early-Stage (0-20 employees, <$2M ARR)** At this stage, your primary need is *speed and simplicity*. You need a CRM that doesn't require a dedicated admin, offers intuitive UX for non-technical users, and provides immediate value without extensive configuration. Your evaluation should prioritize: - Time-to-value (can reps start using it within 1-2 days?) - Mobile-first design for field sales teams - Built-in email/calling without third-party integrations - Transparent pricing with no hidden scaling costs
**Scale-Up (20-200 employees, $2M-$50M ARR)** You're transitioning from founder-led sales to repeatable processes. Your CRM needs to support specialization (SDRs, AEs, CSMs) while maintaining flexibility as you refine your go-to-market motion. Key evaluation criteria: - Workflow automation and pipeline customization - Role-based permissions and team collaboration features - Integration ecosystem (marketing automation, support platforms, data warehouses) - Reporting and forecasting capabilities for leadership visibility
**Enterprise (200+ employees, $50M+ ARR)** At this scale, CRM becomes mission-critical infrastructure requiring governance, compliance, and cross-functional orchestration. Your evaluation must address: - Multi-region deployment with data residency controls - Advanced security (SSO, SAML, audit logs, field-level encryption) - Customization depth (custom objects, complex workflows, API extensibility) - Vendor stability and enterprise SLAs
**Critical Insight**: Many organizations select CRMs based on their *current* state rather than their *12-18 month trajectory*. If you're growing rapidly, choosing a "simple" CRM that you'll outgrow in 12 months creates expensive churn. Conversely, implementing an enterprise CRM when you have 15 employees creates unnecessary complexity that kills adoption.
**Phase 2: Map Your Non-Negotiable Requirements vs. Nice-to-Haves**
In CRM evaluations, I've seen teams create 50+ item feature lists that obscure what actually matters. Instead, use this prioritization framework:
**Tier 1: Deal-Breakers (Must-Have)** These are requirements where compromise means the CRM fundamentally won't work: - Industry-specific compliance (e.g., HIPAA for healthcare, FINRA for financial services) - Data residency constraints (e.g., EU data must stay in EU data centers) - Core workflow support (e.g., if you run complex quote-to-cash processes, the CRM must support CPQ) - Integration requirements (e.g., if your business runs on Salesforce Marketing Cloud, you need native integration)
**Tier 2: High-Impact (Should-Have)** Features that significantly improve efficiency but have workarounds: - Email sequence automation (can be handled by external tools) - Advanced reporting (can supplement with BI tools) - Mobile app quality (can use web interface if needed)
**Tier 3: Optimization (Nice-to-Have)** Features that improve experience but don't affect core functionality: - AI-powered lead scoring - Built-in phone dialer - Customizable dashboards
**Common Mistake**: Teams often elevate "nice-to-haves" to "must-haves" during vendor demos, leading to over-buying. A CRM with 200 features you'll never use is worse than one with 30 features you'll actually adopt.
**Phase 3: Model Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Across 3 Years**
CRM pricing is intentionally opaque. Vendors advertise low per-user/month rates but generate revenue through:
**Pricing Scaling Mechanisms**: 1. **User tier jumps**: Many CRMs offer "Starter" plans at $10-15/user/month but force you to "Professional" ($50-80/user/month) once you need basic automation or API access 2. **Contact/record limits**: Some CRMs charge based on total contacts or records stored, creating unpredictable costs as your database grows 3. **Feature gating**: Essential capabilities (custom fields, workflow automation, reporting) locked behind higher tiers 4. **Add-on fees**: Phone systems, advanced analytics, premium support, additional storage 5. **Integration costs**: API call limits, third-party connector fees, middleware requirements
**TCO Calculation Template**: ``` Year 1: - Base subscription: [Users] × [Per-user cost] × 12 months - Implementation: Data migration + configuration + training ($5K-$50K depending on complexity) - Integrations: Third-party tools + middleware + developer time - Hidden costs: Premium support, additional storage, phone system add-ons
Year 2-3: - Subscription growth: Account for 20-30% annual user growth - Tier escalation: Model cost increase when you hit feature limits - Maintenance: Ongoing admin time, additional training, integration updates - Opportunity cost: Revenue impact if adoption fails or system doesn't scale
Total 3-Year TCO = Sum of above ```
**Reality Check**: If a vendor quotes $25/user/month, your actual TCO is likely $75-$120/user/month when including all factors. Organizations that skip TCO modeling face budget surprises that erode executive support for the CRM initiative.
**Phase 4: Assess Vendor Lock-in and Exit Risk**
CRM vendors profit from switching costs. Before committing, evaluate your exit strategy:
**Data Portability**: - Can you export all data (including custom fields, attachments, activity history) in standard formats (CSV, JSON)? - Are there API rate limits that make bulk export impractical? - Does the vendor provide migration assistance, or will you need third-party tools?
**Integration Dependencies**: - If you've built 15 integrations via the CRM's API, how portable are those workflows? - Are you using proprietary features (custom objects, unique workflow logic) that don't map to other CRMs?
**Contract Terms**: - What are the cancellation terms? (Many enterprise contracts require 90-day notice) - Are there data retention policies after cancellation? - Do you own your data, or does the vendor claim rights to aggregated insights?
**Migration Cost Estimate**: For a mid-sized company (50-100 users, 3 years of data), expect: - Data migration: $10K-$30K - Workflow rebuild: $20K-$50K - Integration re-implementation: $15K-$40K - Training and adoption: $10K-$25K - **Total switching cost: $55K-$145K**
This isn't an argument against CRM adoption—it's a call for **informed commitment**. Choose a CRM you can live with for 5+ years, not just one that looks good in a 30-minute demo.

*This framework guides organizations through a systematic CRM evaluation process, from assessing maturity level to running proof-of-concept tests.*
**Phase 5: Run a Structured Proof-of-Concept (POC)**
Most organizations skip rigorous testing and rely on vendor demos, which showcase ideal scenarios rather than real-world complexity. A proper POC should:
**Test Real Workflows**: - Import a sample of actual customer data (anonymized if needed) - Have 3-5 reps perform their daily tasks for 2 weeks - Measure time-to-complete vs. current process
**Evaluate Integration Complexity**: - Connect your actual email, calendar, and key business systems - Test data sync reliability and latency - Identify API limitations or integration gaps
**Assess Adoption Friction**: - Observe where reps get stuck or frustrated - Measure how much training is required for basic proficiency - Identify workflow mismatches that require workarounds
**Validate Vendor Claims**: - Test reported features (many are vaporware or poorly implemented) - Verify performance with realistic data volumes - Confirm compliance certifications and security controls
A 2-week POC with 5 users costs ~$2,000-$5,000 in time investment but can prevent a $100,000+ mistake.
---
## Critical Decision Factors That Determine CRM Success or Failure
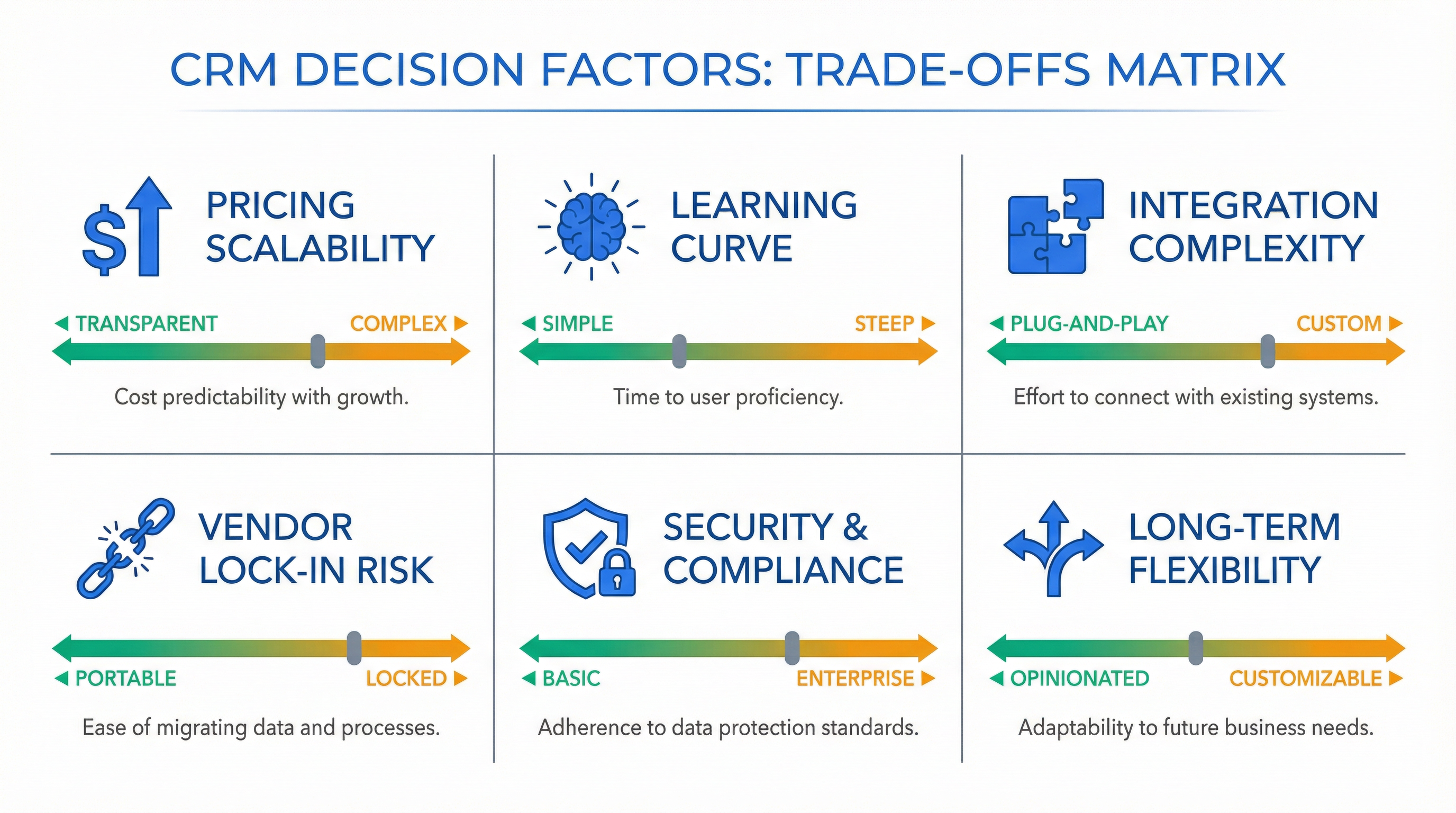
*Every CRM choice involves trade-offs. This matrix helps decision-makers understand the spectrum of options across six critical dimensions.*
Beyond features and pricing, these factors separate successful CRM implementations from failures:
**Factor 1: Architectural Philosophy (Opinionated vs. Flexible)**
CRMs fall on a spectrum:
**Opinionated CRMs** (e.g., Close, Pipedrive): - Enforce specific sales methodologies and workflows - Faster time-to-value with less configuration - Limited customization—you adapt to the tool's logic - **Best for**: Teams with straightforward sales processes, limited technical resources
**Flexible CRMs** (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot): - Highly customizable with custom objects, fields, and workflows - Requires significant configuration to match your process - Risk of over-customization leading to technical debt - **Best for**: Complex sales processes, unique industry requirements, technical teams
**Trade-off**: Opinionated CRMs deliver faster ROI but constrain future flexibility. Flexible CRMs offer unlimited customization but require ongoing admin investment. Most organizations underestimate the *maintenance burden* of flexible CRMs.
**Factor 2: Integration Ecosystem and API Quality**
Your CRM doesn't operate in isolation—it must connect to marketing automation, support platforms, billing systems, data warehouses, and more. Evaluate:
**Native Integrations**: - Does the CRM offer pre-built connectors to your existing stack? - How reliable are these integrations? (Check user reviews for sync issues) - Are integrations included in base pricing or sold as add-ons?
**API Capabilities**: - RESTful API with comprehensive documentation? - Rate limits (requests per day/hour)—will you hit limits during normal operations? - Webhook support for real-time data sync? - Bulk API for large data operations?
**Integration Maintenance**: - Who maintains integrations when APIs change? (Vendor, third-party, or your team?) - Are there middleware requirements (Zapier, Workato, custom code)?
**Warning**: Many CRMs advertise "1,000+ integrations" but rely on third-party middleware (Zapier) that adds cost, latency, and failure points. Native integrations are far more reliable.
**Factor 3: Data Governance and Compliance**
For organizations in regulated industries or serving global markets, compliance isn't optional:
**Data Residency**: - Where are your CRM servers located? (US, EU, APAC) - Can you specify data residency per customer/region? - Does the vendor offer regional data centers?
**Compliance Certifications**: - SOC 2 Type II (security controls) - ISO 27001 (information security) - GDPR compliance (EU data protection) - Industry-specific: HIPAA (healthcare), FINRA (financial services), FedRAMP (government)
**Security Controls**: - Encryption at rest and in transit - Field-level encryption for sensitive data - Role-based access control (RBAC) granularity - Audit logs for compliance reporting - SSO/SAML support for enterprise authentication
**Data Ownership**: - Who owns customer data? (You should) - Can the vendor use your data for AI training or benchmarking? - What happens to data after contract termination?
**Reality**: Many SMB-focused CRMs lack enterprise-grade compliance features. If you're in healthcare, finance, or government, your viable options shrink significantly.
**Factor 4: User Experience and Adoption Drivers**
The best CRM is the one your team actually uses. Adoption depends on:
**Cognitive Load**: - How many clicks to complete common tasks? - Is the interface intuitive for non-technical users? - Does mobile UX match desktop functionality?
**Workflow Alignment**: - Does the CRM match how your team actually works, or force artificial processes? - Can reps complete tasks without leaving the CRM (email, calling, task management)? - Are there friction points that encourage workarounds (e.g., using spreadsheets instead)?
**Value Perception**: - Do reps see immediate personal benefit (easier pipeline management, faster deal closure)? - Or does the CRM feel like "admin work for management reporting"?
**Training Requirements**: - Can new hires become proficient in 1-2 days, or does it require weeks? - Is ongoing training needed as the CRM evolves?
**Adoption Killer**: CRMs that optimize for "manager visibility" at the expense of "rep productivity" fail. If data entry feels like busywork, reps will find ways around it.
**Factor 5: Vendor Stability and Roadmap Alignment**
CRM is a long-term commitment. Assess vendor health:
**Financial Stability**: - Is the vendor profitable, or burning VC cash? - Recent funding rounds or acquisition rumors? - Customer churn rates (if disclosed)?
**Product Roadmap**: - Is the vendor investing in areas that matter to you? - Are they chasing trends (AI hype) or solving real problems? - How frequently do they ship meaningful updates?
**Customer Support Quality**: - What support tiers are available? (Email-only, phone, dedicated CSM) - Response time SLAs? - Community forums and documentation quality?
**Exit Risk**: - If the vendor gets acquired, will the product be maintained or sunset? - Are there viable alternatives if you need to migrate?
**Red Flags**: Vendors with declining market share, frequent leadership changes, or pivot strategies often deprioritize existing customers.
---
## How CRM Requirements Differ by Company Scale and Maturity
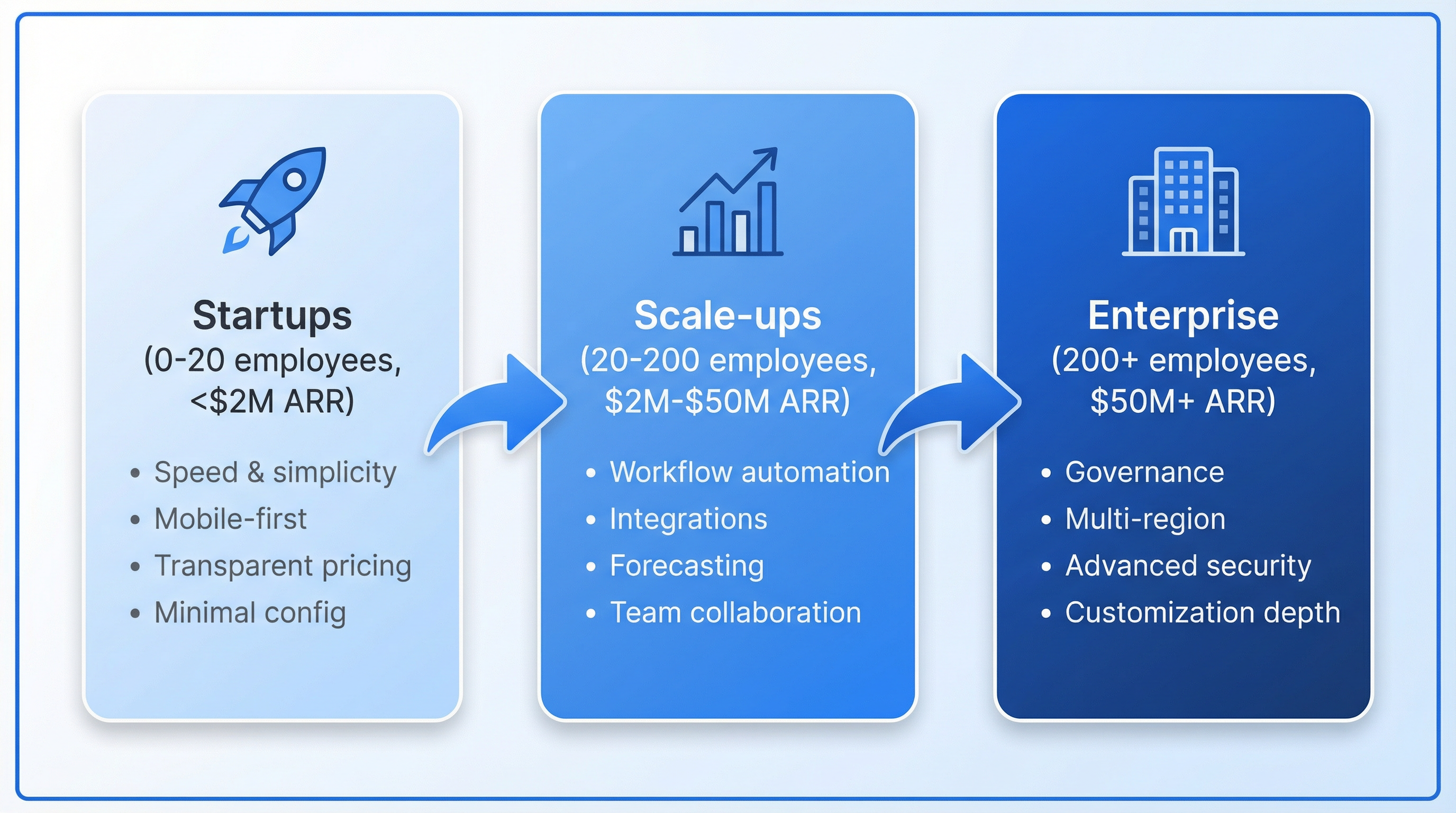
*CRM requirements evolve as organizations grow. This framework shows how priorities shift from speed and simplicity to governance and customization.*
One of the biggest mistakes in CRM selection is ignoring your organization's lifecycle stage. Here's how requirements evolve:
**Startups and Small Businesses (0-20 employees)**
**Primary Goal**: Speed and simplicity. You need immediate productivity, not a 6-month implementation.
**Key Requirements**: - **Minimal configuration**: Should work "out of the box" with minimal setup - **Transparent pricing**: No hidden costs or surprise tier jumps - **Mobile-first**: Founders and early reps work remotely and on-the-go - **Built-in communication**: Email, calling, SMS without third-party tools - **Affordable scaling**: Pricing should grow linearly with team size
**Common Mistakes**: - Over-buying enterprise features you won't use for 3+ years - Choosing CRMs that require dedicated admins - Underestimating training time for complex platforms
**Decision Heuristic**: If you can't get 80% value within the first week, it's the wrong CRM for your stage.
**Scale-Ups and Growth Companies (20-200 employees)**
**Primary Goal**: Process standardization and cross-functional alignment. You're transitioning from ad-hoc sales to repeatable systems.
**Key Requirements**: - **Workflow automation**: Reduce manual tasks as volume increases - **Pipeline customization**: Support evolving sales processes and deal stages - **Team collaboration**: Visibility across SDRs, AEs, CSMs, and leadership - **Integration ecosystem**: Connect marketing automation, support, billing, analytics - **Forecasting and reporting**: Leadership needs pipeline visibility and revenue predictability
**Common Mistakes**: - Implementing enterprise CRMs before you have processes to automate - Over-customizing workflows that change every quarter - Neglecting change management during rapid hiring
**Decision Heuristic**: Choose a CRM that supports your 12-18 month roadmap, not your current state. You'll outgrow "simple" CRMs faster than you expect.
**Enterprises and Large Organizations (200+ employees)**
**Primary Goal**: Governance, compliance, and global orchestration. CRM becomes mission-critical infrastructure.
**Key Requirements**: - **Multi-region deployment**: Data residency, localization, regional compliance - **Advanced security**: SSO, SAML, field-level encryption, audit logs - **Customization depth**: Custom objects, complex workflows, API extensibility - **Enterprise SLAs**: Dedicated support, uptime guarantees, disaster recovery - **Vendor stability**: Long-term roadmap alignment and financial health
**Common Mistakes**: - Underestimating implementation complexity (6-12 month timelines) - Insufficient change management across distributed teams - Over-customization leading to technical debt and upgrade challenges
**Decision Heuristic**: At enterprise scale, CRM selection is a 12-18 month process involving IT, security, compliance, and business stakeholders. Rushing leads to expensive re-implementations.
---
## Global Market Considerations: Compliance, Data Residency, and Localization
For organizations operating across borders, CRM selection intersects with complex regulatory requirements:
**GDPR and EU Data Protection**
If you serve EU customers, your CRM must support: - **Data residency**: EU customer data stored in EU data centers - **Right to erasure**: Ability to permanently delete customer data on request - **Data portability**: Export customer data in machine-readable formats - **Consent management**: Track and enforce marketing consent preferences - **Data processing agreements (DPAs)**: Vendor must sign GDPR-compliant DPAs
**Vendor Landscape**: Not all CRMs offer EU data residency. Verify before commitment.
**Industry-Specific Compliance**
**Healthcare (HIPAA)**: - Business Associate Agreement (BAA) required - Encryption of Protected Health Information (PHI) - Audit logs for PHI access - Limited CRM options: Salesforce Health Cloud, HubSpot (with BAA), specialized healthcare CRMs
**Financial Services (FINRA, SEC)**: - Communication archiving and retention (7+ years) - Audit trails for customer interactions - Compliance with Regulation S-P (customer privacy)
**Government (FedRAMP)**: - Authorized cloud service providers only - Extremely limited CRM options (Salesforce Government Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics)
**Localization Requirements**
**Language Support**: - UI localization for global teams - Multi-language customer data (names, addresses, notes) - Regional date/time/currency formats
**Regional Business Practices**: - Tax and invoicing requirements vary by country - Address formats and validation - Communication preferences (email vs. WhatsApp vs. WeChat)
**Decision Impact**: Compliance requirements can eliminate 70-80% of CRM options. Start with compliance constraints, then evaluate features.
---
## Common Questions About CRM Software Selection
**How long does CRM implementation typically take?**
**Realistic Timelines**: - **Simple CRM (Pipedrive, Close)**: 2-4 weeks for basic setup, 2-3 months for full adoption - **Mid-Market CRM (HubSpot, Zoho)**: 1-3 months for configuration, 4-6 months for full adoption - **Enterprise CRM (Salesforce, Dynamics)**: 3-6 months for implementation, 9-12 months for full adoption
**Why It Takes Longer Than Expected**: - Data migration complexity (cleaning, mapping, validation) - Integration development and testing - Workflow customization and approval cycles - User training and change management - Iterative refinement based on user feedback
**Acceleration Factors**: - Clean, well-structured existing data - Clear process documentation before implementation - Executive sponsorship and change management - Phased rollout (pilot team → full organization)
**Should we build a custom CRM or buy off-the-shelf?**
**Build Custom CRM When**: - Your business model is truly unique (not just "we're special") - Off-the-shelf CRMs lack critical industry-specific features - You have in-house engineering resources for ongoing maintenance - Total cost of building + maintaining < buying + customizing
**Buy Off-the-Shelf When**: - Your sales process is relatively standard - You lack engineering resources for long-term maintenance - You need to move quickly (custom builds take 6-12 months minimum) - You want vendor-supported integrations and updates
**Reality**: 95% of organizations should buy, not build. Custom CRMs become technical debt that distracts from core business.
**How do we ensure CRM adoption across our team?**
**Adoption Strategies That Work**: 1. **Involve reps in selection**: Teams adopt tools they helped choose 2. **Demonstrate personal value**: Show how CRM makes *their* jobs easier, not just management reporting 3. **Minimize data entry**: Automate capture (email sync, call logging, form fills) 4. **Executive modeling**: Leaders must use the CRM visibly and consistently 5. **Gamification**: Leaderboards, activity contests, recognition for CRM power users 6. **Ongoing training**: Not just onboarding—continuous skill development 7. **Feedback loops**: Regular check-ins to address friction points
**Adoption Killers**: - CRM feels like "surveillance" rather than productivity tool - Excessive mandatory fields and busywork - Poor mobile experience for field teams - Lack of integration with daily tools (email, calendar, Slack)
**What's the difference between CRM and marketing automation?**
**CRM Focus**: Managing customer relationships, sales pipeline, and deal progression. Core users are sales and customer success teams.
**Marketing Automation Focus**: Lead generation, nurturing campaigns, email marketing, and lead scoring. Core users are marketing teams.
**Overlap**: Many modern CRMs include basic marketing features, and marketing platforms include basic CRM functionality. For small teams, an all-in-one platform (HubSpot, Zoho) can work. For larger organizations, specialized tools (Salesforce + Marketo, Pipedrive + ActiveCampaign) offer deeper capabilities.
**Decision Factor**: If marketing and sales operate independently, separate tools may be better. If alignment is critical, integrated platforms reduce friction.
**How do we handle CRM data migration from spreadsheets or legacy systems?**
**Migration Process**: 1. **Data audit**: Identify what data exists, where it lives, and what's worth migrating 2. **Data cleaning**: Remove duplicates, standardize formats, fill missing fields 3. **Mapping**: Define how old data structures map to new CRM fields 4. **Pilot migration**: Test with subset of data, validate accuracy 5. **Full migration**: Execute bulk import, verify completeness 6. **Validation**: Spot-check records, confirm relationships and history preserved
**Common Challenges**: - **Duplicate records**: Spreadsheets often have multiple entries for same contact/company - **Inconsistent formatting**: Phone numbers, addresses, dates in various formats - **Lost relationships**: Linking contacts to companies, deals to contacts - **Historical data**: Preserving timestamps, activity history, notes
**Cost Estimate**: Data migration for mid-sized company (10K-50K records) typically costs $5K-$20K in consulting or internal time.
---
## How to Think Rationally About CRM Selection
After 15 years of advising businesses on CRM selection, here's what I've learned:
**There is no "best" CRM**—only the right CRM for your specific context. Organizations fail when they chase feature lists rather than aligning CRM capabilities with their actual needs, constraints, and growth trajectory.
**CRM selection is a risk management exercise**, not a feature optimization problem. Your goal isn't to find the CRM with the most features—it's to minimize the risk of adoption failure, budget overruns, and expensive migrations.
**The most expensive CRM mistake is choosing twice**. Organizations that rush selection often face re-implementation within 18-24 months, incurring switching costs that exceed $100K for mid-sized companies. Invest time upfront in rigorous evaluation.
**Start with constraints, not features**. Before comparing CRMs, define your non-negotiable requirements: compliance mandates, budget limits, technical capabilities, and timeline. These constraints eliminate 70-80% of options, making the remaining decision much simpler.
**Test with real workflows, not vendor demos**. Demos showcase ideal scenarios. Run a 2-week proof-of-concept with actual data and real users to surface friction points before commitment.
**Plan for the 3-year horizon, not today**. If you're growing rapidly, choose a CRM that supports your 18-month roadmap. If you're stable, prioritize simplicity over future flexibility you may never need.
**Adoption is everything**. The most sophisticated CRM is worthless if your team doesn't use it. Prioritize user experience, workflow alignment, and change management over feature depth.
Ultimately, CRM software is infrastructure, not a silver bullet. It amplifies your existing processes—if your sales process is broken, a CRM won't fix it. But when chosen thoughtfully and implemented well, the right CRM becomes a strategic asset that compounds value over years.
---
**About This Guide**: This analysis draws on 15 years of experience advising SMBs, scale-ups, and enterprises on SaaS selection and implementation. It reflects real-world CRM evaluations across industries, company sizes, and go-to-market models. No CRM vendors sponsored this content.